马来西亚政府坚信特许经营产业在马来西亚的GDP发展中扮演着重要的角色,其政府通过“国内贸易和消费事务部”,以及“马来西亚特许经营协会”支持的“国家企业有限公司”(Perbadanan Nasional Berhad, PNS),共同引入和推进了许多项目,以促进整体环境加速往高质量且具有竞争力的特许经营网络发展。具体项目包括但不限于特许经营融资计划(Franchise Financing Scheme),特许经营发展援助基金(the Franchise Development Assistance Fund),本地特许经营产品发展计划(Local Franchise Product Development Programme),这些激励旨在将马来西亚打造为东盟区域特许经营产业中心。
The Malaysian government firmly believes that the franchising sector plays a vital role in the country's GDP growth. Through the Ministry of Domestic Trade and Consumer Affairs (MDTCA) and Perbadanan Nasional Berhad (PNS), a government-linked company supported by the Malaysian Franchise Association, numerous initiatives have been introduced to accelerate the development of a high-quality and competitive franchising environment. These initiatives include, but are not limited to, the Franchise Financing Scheme, the Franchise Development Assistance Fund, and the Local Franchise Product Development Programme. These incentives are designed to establish Malaysia as a regional hub for franchising in ASEAN.
根据《马来西亚特许经营法》(下称“《特许经营法》”)(Franchise Act, FA),特许经营是一种基于二者或者多者之间的合同或者协议行为。特许经营权人依据特许经营制度授权特许经营受权人权利开展商业活动,并由特许经营权人决定具体协议内容。一般来说,包括授予特许经营受权人使用任何特许经营权人所有的商标、机密信息、知识产权,以及接触贸易秘密。
Pursuant to the Franchise Act (hereinafter referred to as the "FA"), franchising refers to a contractual or agreement-based relationship between two or more parties. Under the franchise system, the franchisor grants the franchisee the right to carry out business activities in accordance with the franchisor’s established system. This usually includes the right to use the franchisor’s trademarks, access trade secrets, and utilize proprietary information or intellectual property owned by the franchisor.
马来西亚的特许经营一般是由私营有限公司为法人形式载体,在马来西亚,公司注册管理的机构为马来西亚公司委员会(Suruhanjaya Syarikat Malaysia, SSM),所有的公司注册都将在SSM的官方网站上操作以节约公司设立成本。
Franchises in Malaysia are generally operated through private limited companies. The Companies Commission of Malaysia (Suruhanjaya Syarikat Malaysia, SSM) is the statutory body responsible for company registration. All registrations must be carried out online via SSM’s official portal to reduce incorporation costs.
自2004年12月1日以来,所有外国经销贸易都必须获得来自“国内贸易和消费者事务部”下的经销贸易委员会(简称“经委会”)的批准。经销贸易商包括整销贸易商、零售商、特许经营商、直接销售商、产品制造商和供应商,这些商事主体将他们的货物销往马来西亚国内市场,同时他们的销售代表或者代理成员属于国际跨国贸易公司。根据国家政策,大型综合商业体中至少应有30%的马来本地人参股。
Since 1 December 2004, all foreign entities engaged in distributive trade must obtain approval from the Distributive Trade Committee (DTC) under the MDTCA. Distributive traders include wholesalers, retailers, franchisors, direct sellers, manufacturers, and suppliers who sell goods in the Malaysian domestic market and whose representatives or agents operate as part of international or multinational corporations. In line with the National Development Policy, at least 30% of equity in large-scale commercial complexes must be held by Bumiputera (indigenous Malaysians).
此外,外国所有的公司若从事整销、零售、贸易、进出口、餐饮和特许经营事项前,必须取得整销和零售执照(Whole sale and Retail trade licence, WRT)。而外国公司想要申请WRT执照,其公司最低实缴注册资金必须在100万马来西亚林吉特,该执照将在1-2个月办理获得。
Furthermore, foreign-owned companies engaging in wholesale, retail, trading, import/export, food and beverage, or franchising activities must obtain a Wholesale and Retail Trade (WRT) Licence. To qualify, the foreign company must have a minimum paid-up capital of RM 1 million, and the application process typically takes 1 to 2 months.
值得注意的是,“特许经营权人和本地特许经营受权人必须在授权其他分店前,其自有直营的销售点必须在最近3年盈利”,该条规定并没有以成文法的形式在《特许经营法》体现,但是有权机关会根据《特许经营法》第十八条披露文件规定,以前述盈利标准审查特许经营权人和主要特许经营受权人过去3年的财务文件是否达到要求。
A commonly applied but unwritten rule stipulates that a franchisor and its local master franchisee must demonstrate profitability in at least one directly operated outlet for the past three years before authorizing sub-franchising. Although this is not codified in the FA, regulators may review the franchisor’s and master franchisee’s financial records over the past three years based on the disclosure requirements under Section 18 of the FA.
与中国特许经营实践相似,马来西亚特许经营中也存在“先合同披露义务”。在特许经营权转授结构的情况下1,当地主特许经营商负责向次级特许经营商提供售前披露。当地主特许经营商必须披露其为“主特许经营商,而非所涉特许经营业务的特许人,并且商标属于外国特许人”。
Similar to franchising practices in China, Malaysia imposes pre-contractual disclosure obligations. In a sub-franchising structure, the master franchisee is responsible for disclosing relevant information to sub-franchisees. The master franchisee must clarify that it acts as a master franchisee, not the original franchisor, and that the trademarks involved are owned by a foreign franchisor.
根据《特许经营法》第五十四条,外国特许权人在向主特许经营商出售特许经营权之前应已提交特许经营申请,因此所有与运营和经验相关的所有相关信息都应在该申请期间提供给注册机关。对于披露的时间,《特许经营法》第十六条规定,特许人必须每年更新披露文件,并在特许经营业务财政年度结束后的6个月内提交。
Under Section 54 of the FA, a foreign franchisor must submit a franchise registration application before granting any rights to a local master franchisee. All relevant operational and experiential information must be submitted during the registration process. According to Section 16, the franchisor must update its disclosure documents annually and submit them within six months after the end of its financial year.
关于特许权人的披露义务。根据《特许经营法》第十五条规定,特许权人必须在加盟商与特许权人签署“特许经营协议”前至少10天向加盟商提交一份加盟协议和披露文件的副本。该项披露义务在协议期限届满续签时仍须遵循,即向加盟商披露相关文件。
Under Section 15 of the FA, a franchisor must provide the prospective franchisee with a copy of the franchise agreement and disclosure documents at least 10 days before execution of the franchise agreement. This requirement also applies when renewing an existing franchise agreement upon expiry.
一般来说应当披露的内容如下:
The disclosure document should generally include the following information:
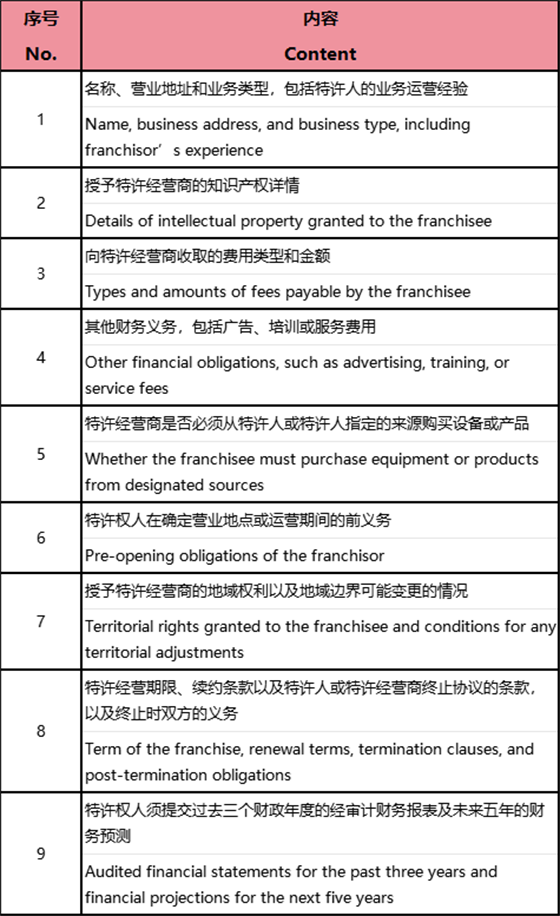
最后,关于特许经营关系的终止。特许权人仅可在《特许经营法》规定的某些情况下终止特许经营关系。例如,《特许经营法》第三十一条规定,特许权人不得在到期日之前终止特许经营协议,但正当理由除外。可见,终止条件为“期限届满2”和“正当理由”。
Finally, with respect to termination of the franchise relationship, the franchisor may only terminate the agreement under specific circumstances provided under the FA. For example, Section 31 stipulates that a franchisor may not terminate the franchise agreement before its expiry except for good cause. Thus, the permissible grounds for termination include expiration of the term and good cause.
其中“正当理由”(Good Cause)包括:(1)加盟商未能遵守特许加盟协议的任何条款;(2)加盟商未能在特许权人书面通知规定的期限内(该期限不得少于14天)对其违约行为进行补救。
“Good cause” includes: The franchisee’s failure to comply with any terms of the franchise agreement; The franchisee’s failure to remedy a breach within no less than 14 days of receiving written notice from the franchisor.
除上述以外,正当理由还包括以下情形:(1)经营者将特许经营权转让给债权人或其他利益相关方,或对特许经营资产进行类似处置;自愿放弃特许经营业务;(2)因犯下严重损害特许商商标或其他知识产权相关商誉的刑事罪行而被定罪;(3)连续多次未能遵守特许经营协议的条款。
Other accepted grounds constituting good cause include: Assignment of the franchise business to creditors or other parties, or other forms of disposition of franchise assets; Voluntary abandonment of the franchise business; Conviction for a criminal offence that seriously damages the goodwill associated with the franchisor’s trademark or intellectual property; Repeated failure to comply with the franchise agreement.
总之,马来西亚的特许经营行业是国民经济中富有活力且稳健的组成部分,其发展得益于完善的监管框架,尤其是《特许经营法》。这一法律体系为国内外特许经营商营造了安全透明的环境,推动了多个领域的显著增长,其中餐饮、零售和教育行业尤为突出。
In conclusion, the franchise industry in Malaysia is a dynamic and stable part of the national economy. Its growth can be attributed to a well-established regulatory framework, particularly the Franchise Act. This legal structure has created a safe and transparent environment for both domestic and foreign franchisees, leading to significant expansion across various sectors. Notably, the food and beverage, retail, and education industries have emerged as particularly prominent within this landscape.
近期,马来西亚的特许经营领域也正在发生重大变革。其中一个重要内容是所有特许经营权都将按照新的MyFEX 2.0系统,在2025年8月前进行强制性重新注册,这是政府为简化和现代化注册流程而采取的举措。这一向数字化的转变也体现了行业将更加强调电子商务、数字营销和数据驱动的商业模式。
The franchise sector in Malaysia is currently experiencing significant changes. One of the key developments is that all franchise rights must be re-registered under the new MyFEX 2.0 system by August 2025. This initiative, introduced by the government, aims to simplify and modernize the registration process. Additionally, this shift towards digitalization suggests that the industry will increasingly focus on e-commerce, digital marketing, and data-driven business models.
注释:
1即外国特许人指定当地主特许经营商,而该主特许经营商再在马来西亚指定次级特许经营商。
2特许经营授权期限最少5年。
欢迎关注全国优秀律师事务所湖南通程律师事务所,微信公众号请关注hntcls